Tests on unvulcanised rubber
Wide variety of advanced equipment
With a wide variety of advanced equipment in the laboratory, ERT can test or measure the following properties of rubber:
The tests are carried out as standard in accordance with ASTM, DIN and/or ISO standards. We can also meet any customer-specific test requirements.
Would you like more information about testing for unvulcanised rubber?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
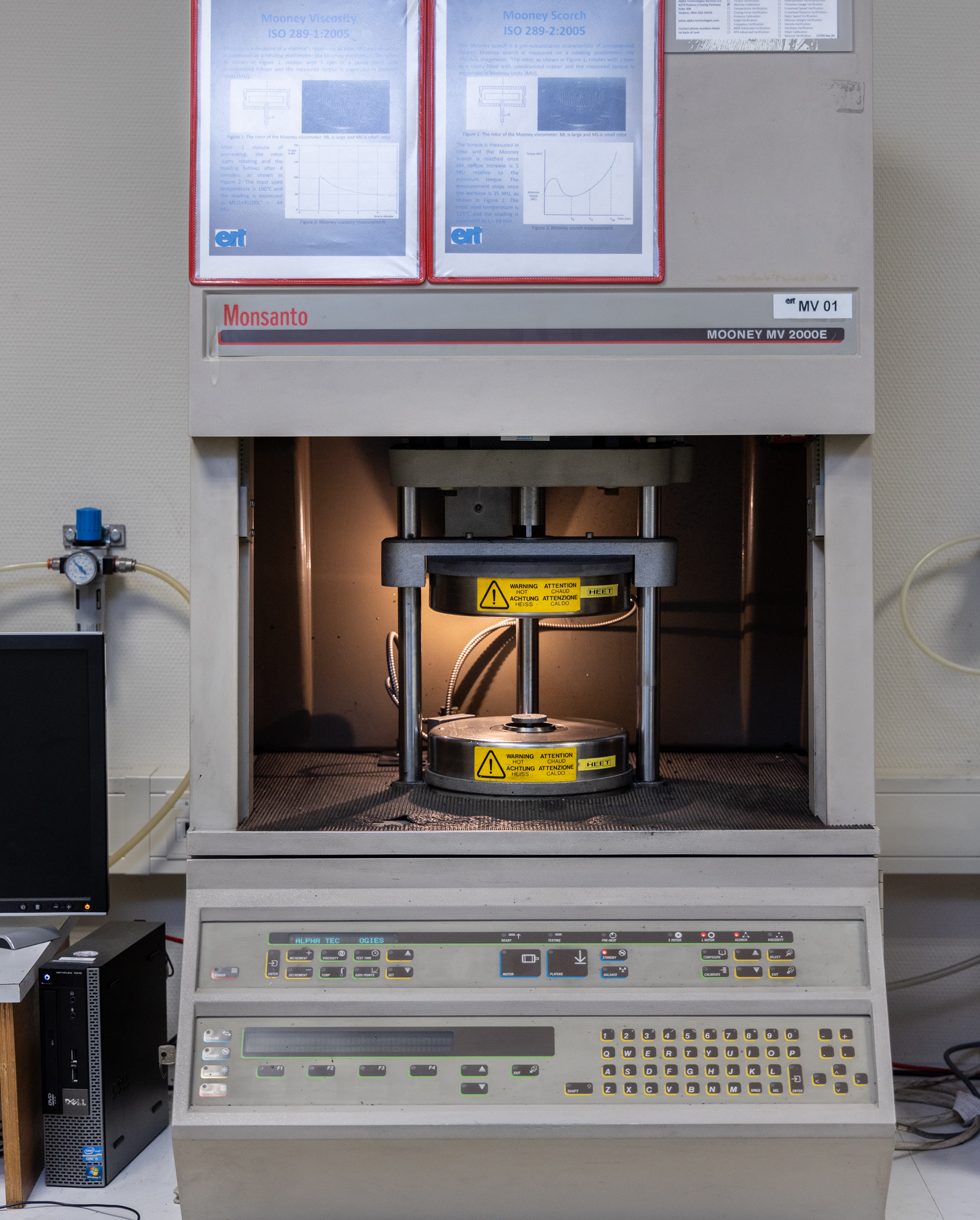
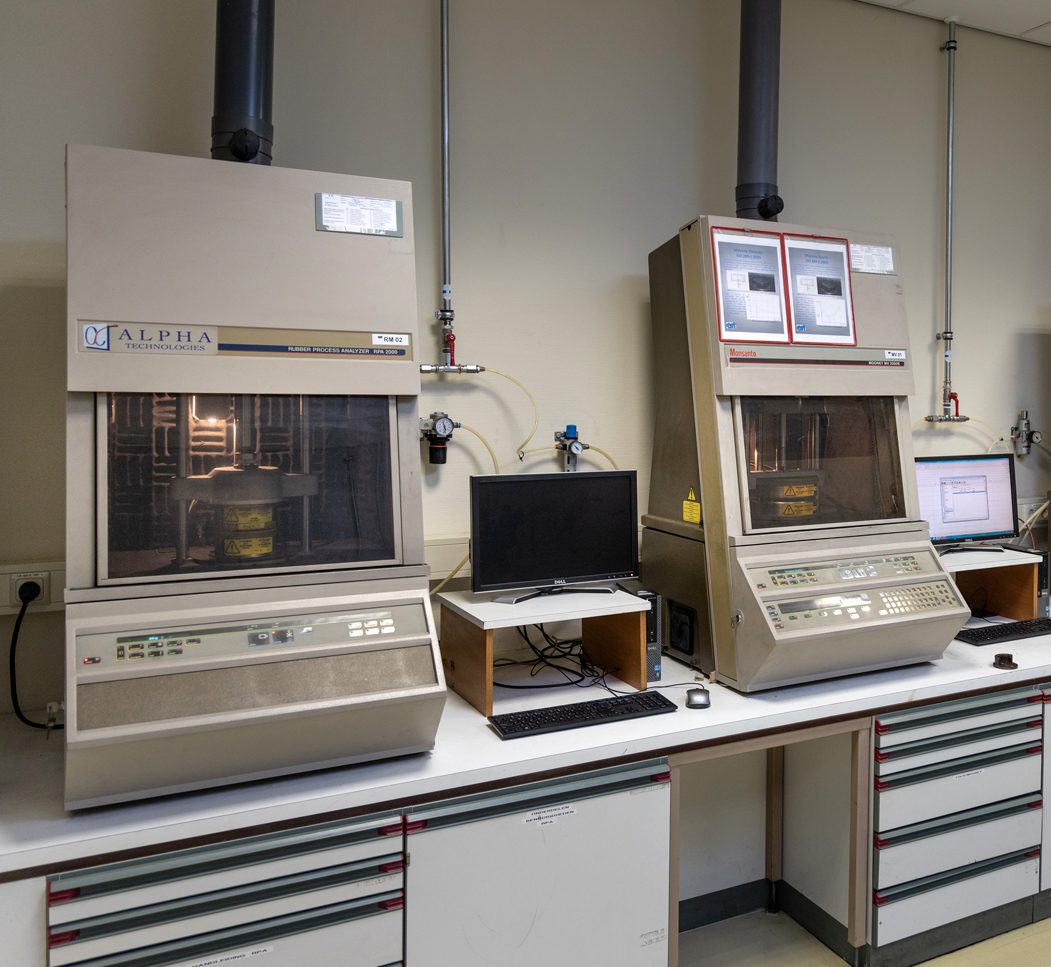
Mooney viscosity, scorch and relaxation test of rubber compounds (ISO289-1 to 4)
Mooney viscometer (MV2000E)
In order to be processable in practice, the viscosity of unvulcanised rubber compounds must not be too high. Secondly, they must have a sufficient flow rate. This is the time necessary for a compound to flow and take the shape of a mould. This must occur before vulcanisation starts.
The tests are carried out according to ISO standards 289-1 to 4, unless otherwise desired.
Would you like to know more about mooney viscosity?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
Vulcanization characteristics (MDR2000E) ISO6502
Determination of processing characteristics of uncured rubber compounds at the desired vulcanization temperature, including the scorch time, ts2 (maximum processing time to fill a mould cavity), optimum vulcanization time, t90, minimum and maximum torque and Delta S.
These are compound-specific processing properties that determine, amongst other things, the temperature, time and degree of vulcanization.
The tests are carried out according to ISO standard 6502, unless otherwise desired.
Interested in vulcanization characteristics?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
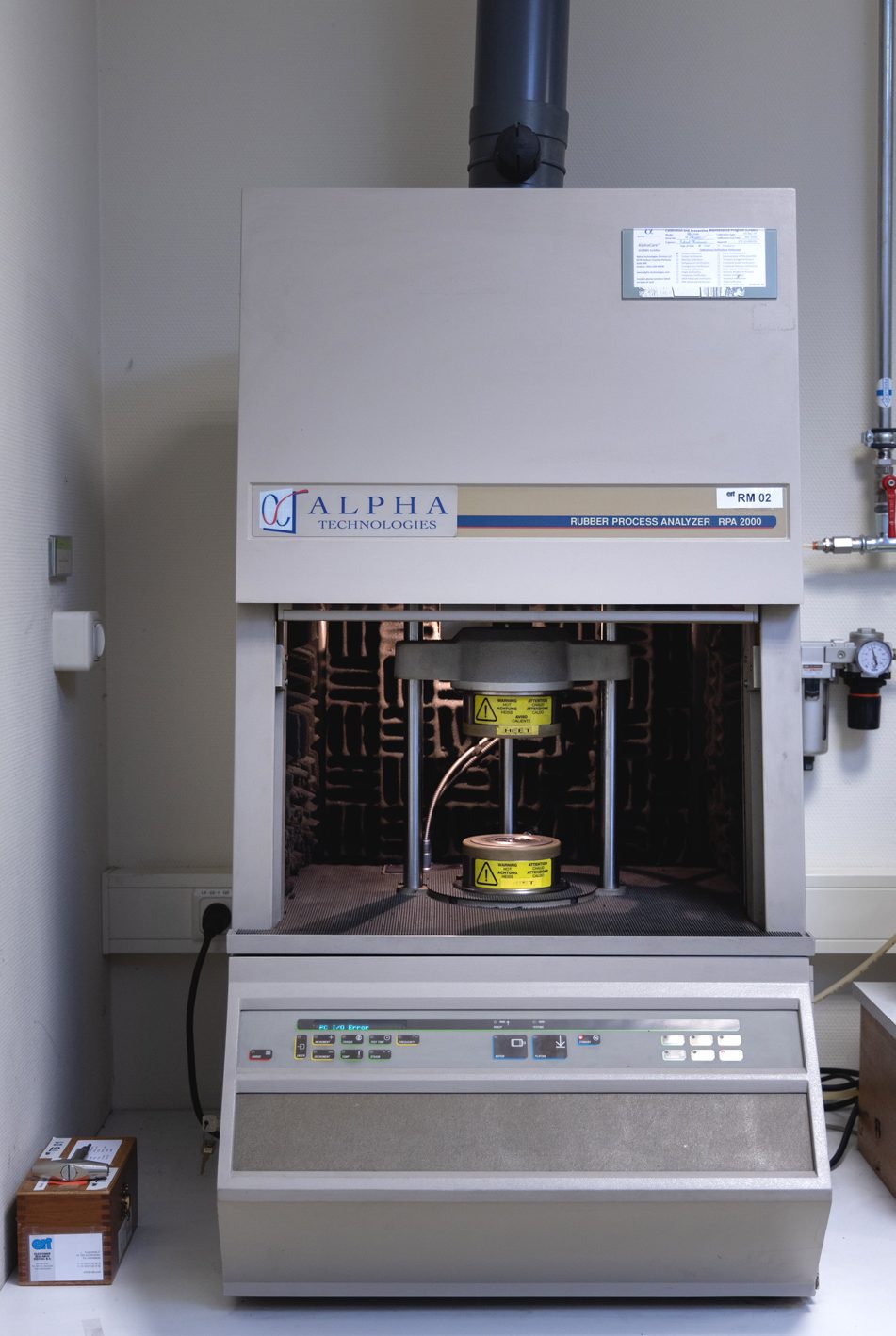


Rubber Process Analyser, RPA
(e.g. Payne effect)
The Rubber Process Analyser (RPA) is a dynamic mechanical rheological tester developed to analyse raw elastomers and unvulcanised compounds. The machine can make measurements up to 230°C, from 0.02 to 50Hz and from 1 to 1250% elongation. It is often used to determine the Payne effect, amongst other things.
The Payne effect is the difference in modulus at relatively low elongation rates. The difference is caused by the so-called 'filler-filler interaction'. During mixing, the filler should be dispersed homogeneously through the compound, which indicates a break-up of agglomerates into primary particles, resulting in a filler network within the polymer network.
For example, silica has a higher filler-filler interaction than carbon black.
The test is carried out according to the ERT 403 in-house test method, unless otherwise desired.
Would you like more information about the Rubber Process Analyser?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
Green strength (ISO9026)
Green strength is a measure of the mechanical properties of an uncured rubber, and depends primarily on the physical and chemical properties of the polymer, as well as filler content. It is a key property for all processing steps, in which the compound is exposed to particular elongation rate.
The test is carried out according to ISO standard 9026, unless otherwise desired.
Want to know more about green strength?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
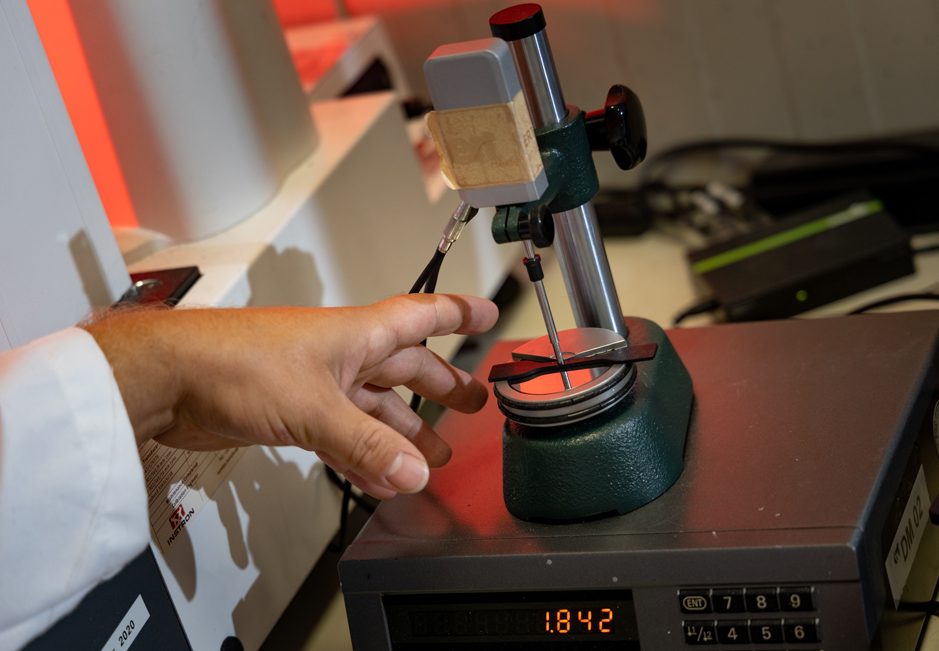
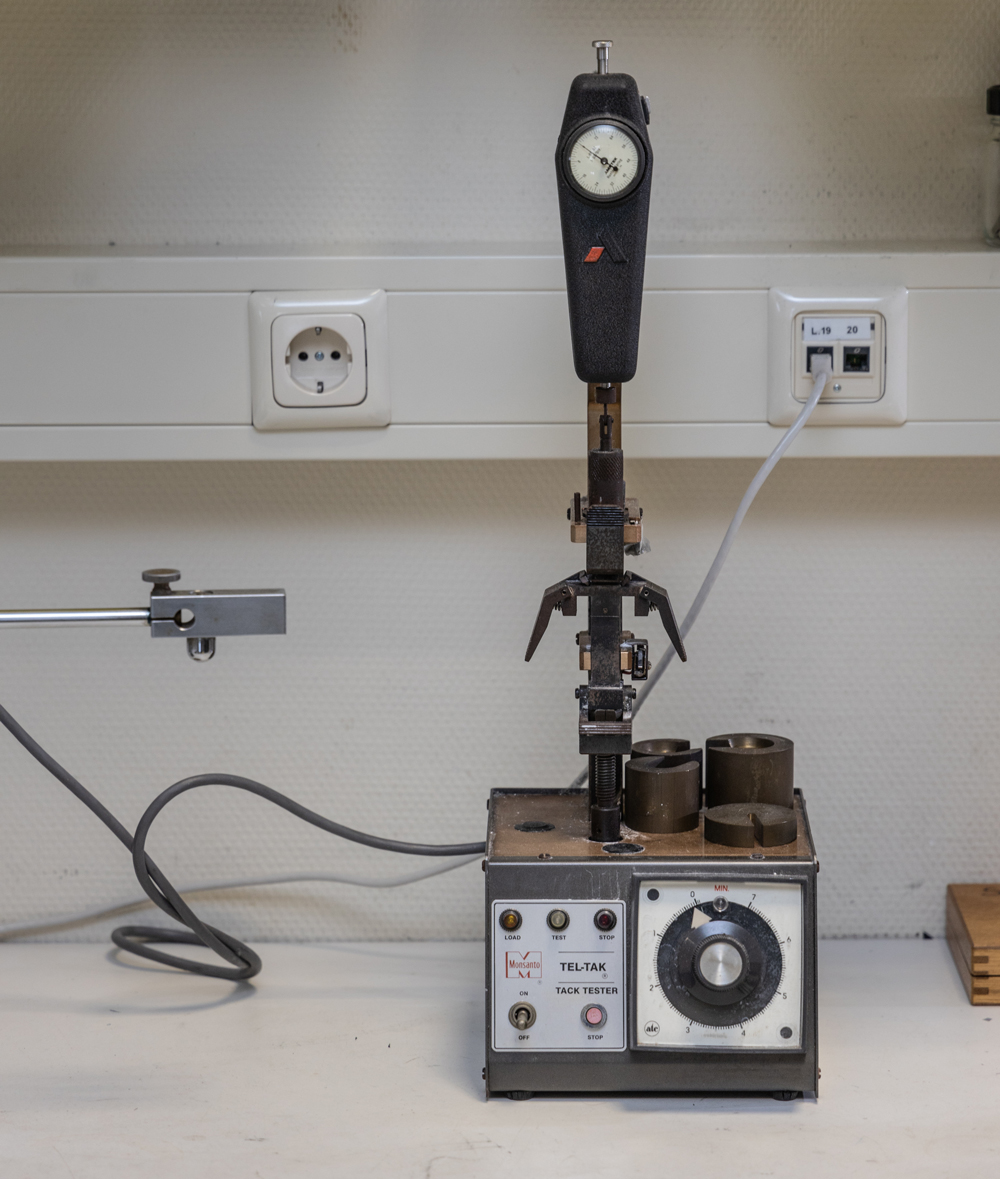


Tack tester of rubber compounds
A mechanical tack tester is used to determine the polymer tack and adhesive properties of the unvulcanised compound.
The test is carried out according to an ERT in-house test method, unless otherwise desired.
Want to know more about tack tester?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
Bound rubber
Bound rubber is the amount of polymer that is physically bound to the filler before vulcanization and cannot be extracted.
The test is carried out according to our ERT in-house test method, unless otherwise desired.
Are you interested in bound rubber?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.


Vulcanisation shrinkage (ISO2577)
Rubber products will always display a degree of shrinkage after vulcanisation. After determining this percentage, it can be taken into account in the dimensions of the mould, so as to get a perfect size.
The test is carried out according to ISO standard 2577, unless otherwise desired.
Do you have a question about vulcanisation shrinkage?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.
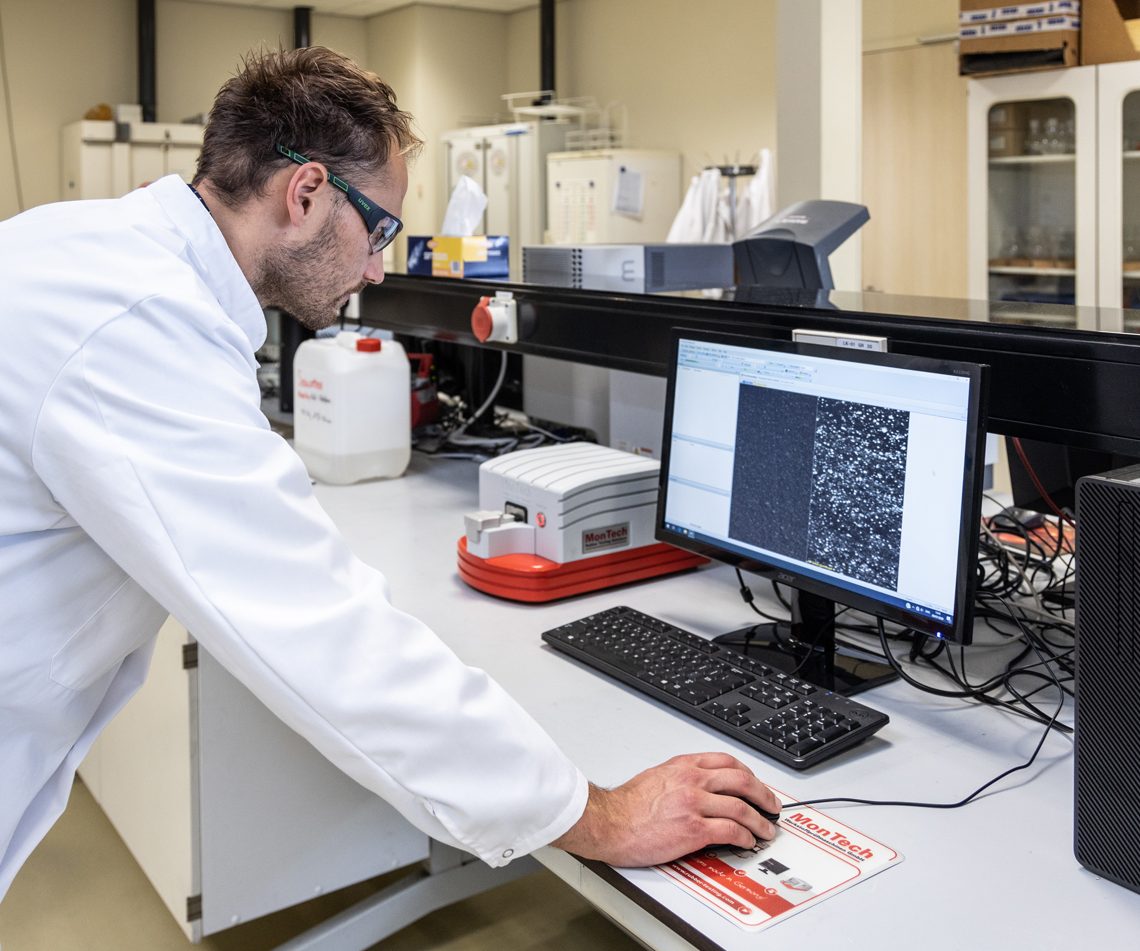
Dispersion of ingredients in rubber compounds
Proper dispersion of ingredients is important to obtain a homogeneously mixed compound. Good dispersion also ensures that all products made from a particular compound batch have the same vulcanisation rate and cross-link density. Measurements of this kind also give insight into the processability of specific ingredients during mixing on the two-roll mill.
The test is carried out according to the ERT 302 in-house test method, unless otherwise desired.
Would you like more information about the dispersion of rubber compounds?
Please leave your details in the contact form at the bottom of this page. We will respond as soon as possible.

Information request about tests on unvulcanised rubber
Privacy
Your information will not be used for any other purpose and will not be provided to third parties. Your data can be deleted at any time. For more information about how we process your data, please see our privacy statement.
We will be happy to help you
Location
Elastomer Research Testing BV
Teugseweg 27
7418 AM Deventer the Netherlands
Postal address
Elastomer Research Testing BV
PO Box 2149
7420 AC Deventer the Netherlands
Contact
E info@ertbv.com
T +31 570 62 46 16
F +31 570 62 57 02

